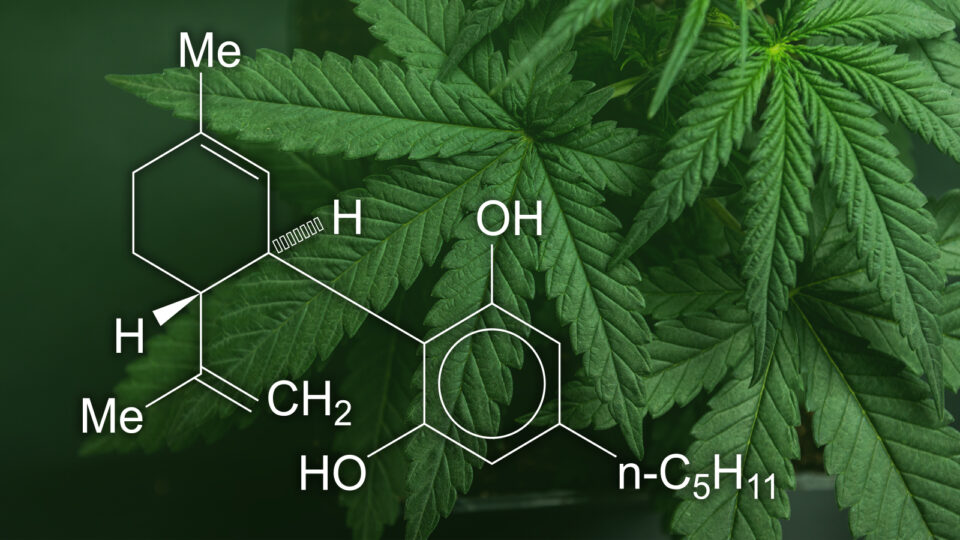
There’s no question that cannabis is a complex plant with hundreds of chemical compounds, of which the most popular and active ones are cannabinoids.
Today the plant has tons of strains that are constantly bred to manipulate the chemical profiles and, in turn, the effects. If you loved the classic OG strains like Pre-98 Bubba Kush, you know they hit differently than the countless modern strains on the streets.
And if you’re wondering, it’s the cannabinoids like THC and CBD that influence the nonstop breeding and here’s why.
Cannabinoids comprise the biggest part of the plant resin extract and can uniquely interact with the body. These compounds have all kinds of effects, many of which are therapeutic.
If you’re still curious about cannabinoids and their effects, this post will help you understand.
What are Cannabinoids?
Cannabinoids are a particular class of compounds initially found in the cannabis plant. Further research has discovered them in animals (including humans) and other plants.
In cannabis, researchers have found more than 60 active cannabinoids with varying effects.
The most well-known and researched of these compounds are cannabidiol (CBD) and delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC). They also happen to be the most prominent cannabinoids in the plant.
Different Types of Cannabinoids and Their Effects
THC and CBD aren’t the only common cannabinoids out of the pack. There are others, and we will discuss each and their effect on the body.
1. Cannabidiol (CBD)

CBD is probably the most popular cannabinoid and one of the only two primary cannabinoids, the other being THC.
The compound is well known for its non-psychotropic nature. Basically, it doesn’t have the same mind-altering effects THC has.
While CBD doesn’t have intoxicating effects, it interacts with the body’s endocannabinoid system just like other cannabinoids. It’s also considered the most powerful cannabinoid with many proven and potential health benefits.
One common effect of CBD is its ability to relieve anxiety and depression. Studies have also proven CBD’s effectiveness in treating chronic pain.
The compound also plays a role in controlling epileptic seizures, which led to the approval of a CBD-based drug for two rare forms of epilepsy.
2. Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)

THC is the other popular cannabinoid known as the primary element in cannabis with psychotropic effects. But its effects don’t stop at giving you a head high. It’s also the only cannabinoid that gives CBD a run for its money.
In fact, THC has proven to be a stronger pain reliever than CBD. It’s also known to uplift moods, and studies show that it can relieve stress and anxiety in low doses.
More effects of THC can be seen in its ability to assist in health problems like:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Neurodegeneration
- Muscle spasms
- Sleep disorders
- Loss of appetite
3. Cannabigerol (CBG)

Recently, cannabigerol entered the spotlight as researchers dug more into it.
If you look into the origins of cannabinoids, you will find that they all have the same source. That source is CBG.
Basically, cannabigerol is the original cannabinoid, which undergoes multiple transformations creating all other cannabinoids. As such, it’s known as the “mother of all cannabinoids.”
CBG affects the body in many ways, and while researchers are just scratching the surface, what they have found is amazing.
The compound has powerful anti-inflammatory and ant-bacterial properties, but it can also regulate sleep and mood and fight cancer-causing cells.
4. Cannabinol (CBN)
When THC degrades, the process creates a new cannabinoid called cannabinol (CBN). The compound can also form when THC is heated at a high temperature. Regardless of the process, CBN exists as a byproduct of THC.
The effects of CBN can be seen in its ability to combat insomnia, inflammation, and loss of appetite. It also acts as an antibiotic.
5. Cannabichromene (CBC)
Cannabichromene is one of the least known cannabinoids that has been making waves in the scientific community, much like cannabigerol. This phytocannabinoid is not mind-altering, and just like CBG, it may be key to a future breakthrough in gastrointestinal cancer.
CBC has powerful anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties. While at the moment, studies are restricted to mice, they reveal positive effects.
In mice, CBC was able to relieve pain and inflammation as well as improve brain function, preventing neurodegeneration.
6. Tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV)

While Tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV) is one of the least known and less abundant cannabinoids, it appears to have much in common with THC. Unlike THC, though, THCV doesn’t seem to have mind-altering effects.
The cannabinoid’s interaction with ECS receptors affects certain nerve cells in the brain and seems to play a role in regulating seizures, diabetes, pain, and other conditions.
While there isn’t much research on the potential of THCV, it’s already emerging as a major cannabinoid with powerful effects.
7. Cannabinodiol (CBND)

Cannabinodiol (CBND) is a derivative of CBD that can also occur through a chemical conversion of CBN. The compound’s concentration in the cannabis plant is exceedingly low, contributing to the lack of enough research on it.
Unlike other cannabinoids, CBND doesn’t interact naturally with the endocannabinoid receptors.
Still, evidence shows that the compound stimulates the ECS indirectly and may play a role in treating emotional and psychological disorders.
8. Cannabicyclol (CBL)

Cannabicyclol (CBL) is one of the minor cannabinoids undergoing research to uncover its properties and effect in humans. The compound is present in trace amounts in the marijuana plant and only forms when cannabichromene (CBC) degrades.
9. Cannabitriol (CBT)

As one of the minor cannabinoids, Cannnabitriol has a low prevalence and is sometimes present and sometimes not, depending on the individual strain.
There isn’t much known about CBT, and there hasn’t been much research on the compound. It appears that the effects of CBT are largely unknown.
However, a small study on THC addiction found that CBT could potentially combat the psychoactive effects of THC. Considering CBT’s chemical structure is similar to that of THC, it’s not surprising that it may influence the effects of the major cannabinoid.
Legal Considerations
It’s essential to recognize that the legal landscape surrounding cannabinoids is intricate and subject to significant variation. The article doesn’t delve into the crucial aspect of the legal status of these compounds. It’s worth emphasizing that the legality of cannabinoids varies not only from country to country but also within different states or regions of the same country. Some jurisdictions have embraced certain cannabinoids for medical or recreational use, while others maintain strict regulations or outright prohibition. For instance, CBD, with low or no THC content, is legal in many places, but THC-rich products may be restricted.
Emerging Research
While the article provides valuable insights into known cannabinoid properties, it’s equally vital to underscore the continuous evolution of cannabis research. Scientists are actively exploring the potential medical applications of cannabinoids that extend beyond current understanding. This dynamic nature of research emphasizes the need for ongoing scientific exploration in the field of cannabis. As new findings emerge, our comprehension of cannabinoids deepens, potentially uncovering innovative therapeutic uses.
This evolving landscape of knowledge highlights the importance of staying informed about the latest developments in cannabinoid research and the legal status of these compounds in your locality. For comprehensive information on cannabinoids and their legal status, consider reliable sources and consult local regulations. Stay updated on the latest insights and legal updates regarding cannabinoids to make informed choices. If you are interested in cannabinoids in Washington DC, visit FastSlice DC.
Final Thoughts
There are over 60 confirmed cannabinoids in the cannabis plant. However, some reports put the figure at over 140. The thing is, cannabis is a complex plant, and scientists continue to uncover more with time.
According to experts, what we know about cannabinoids is surface knowledge, with the future holding much promise.